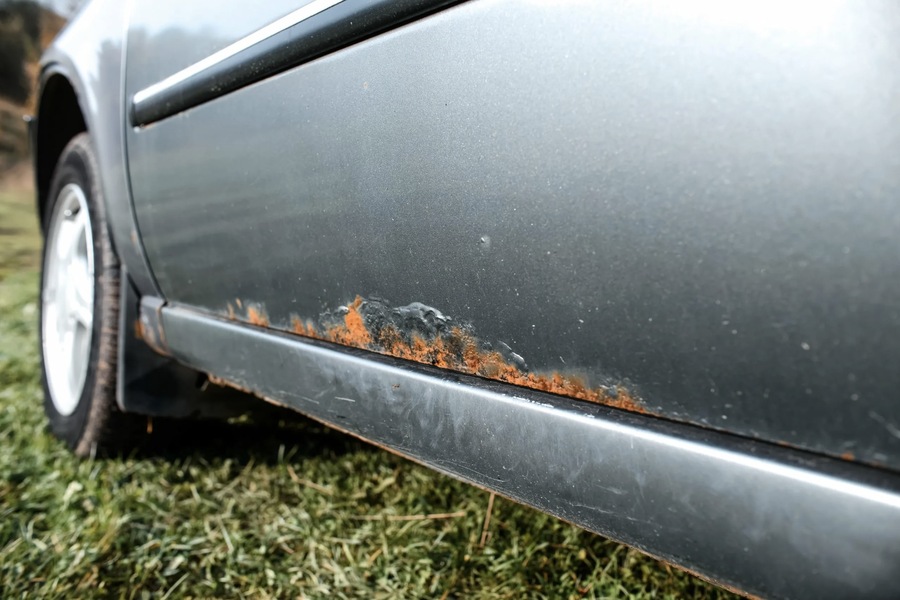
Rust on a car is the result of corrosion, a process where metal deteriorates under the influence of environmental factors. This article will delve into the causes, types, formation, vulnerabilities, preventive measures, and specific challenges related to rust in cars, especially within the context of the UAE. One effective preventive measure is the application of a nano ceramic coating, which provides a durable, protective layer against environmental damage.
Causes of Rust
Rust formation on a car can be attributed to several factors:
- Age and Non-Galvanized Body: Older cars, particularly those with non-galvanized bodies, are more prone to rust. Over time, the protective coatings and paint on a car degrade, exposing the underlying metal to the elements. Non-galvanized bodies lack a protective zinc coating that helps prevent rust.
- Unattended Body Damage: Scratches or dents that are not promptly repaired can become starting points for rust. When the paint layer is breached, moisture and air can come into direct contact with the metal surface, accelerating the corrosion process.
- Exposure to Salt and Humid Climate: Areas with salty air or high humidity accelerate the rusting process. Salt, especially, acts as a catalyst for corrosion by breaking down the protective layers on the car’s surface, leading to quicker and more aggressive rust formation.
Types of Rust
Rust can manifest in different forms, each indicating the progression of corrosion:
- Spot Rust: The initial stage, characterized by small rust spots that can be easily treated to prevent further spread. This type of rust is usually superficial and affects only the top layer of the metal.
- Focal Rust: Over time, spot rust can expand and merge into larger areas, posing a significant threat to the car’s integrity. Focal rust indicates that the corrosion has penetrated deeper into the metal, compromising its strength.
- Structural Rust: At this stage, the metal has deteriorated to the point of forming holes, severely compromising the vehicle’s structural integrity. Structural rust is often indicative of long-term neglect and can render the car unsafe to drive.
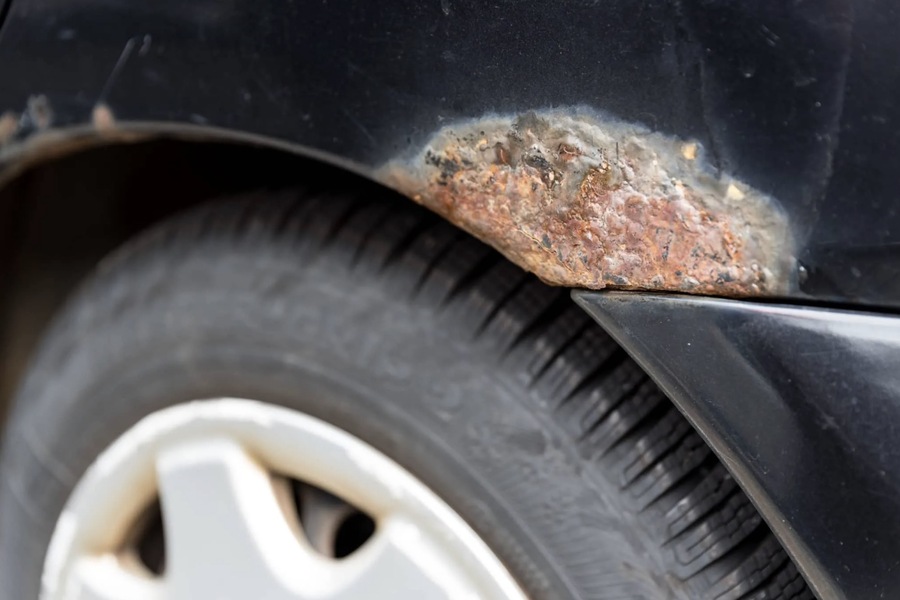

How Rust Forms
Rust forms when iron reacts with oxygen in the presence of water or moist air, creating iron oxides. This chemical reaction is a form of oxidation, which continues as long as moisture and oxygen are present. Unlike some metals, iron oxides do not form a protective layer, allowing the corrosion to penetrate deeper, eventually destroying the metal entirely.
The rusting process can be broken down into several stages:
- Initial Oxidation: Iron reacts with oxygen to form iron (III) oxide, a reddish-brown compound.
- Hydration: The iron oxide reacts with water to form hydrated iron oxide, commonly known as rust.
- Propagation: The rust layer does not protect the underlying metal, allowing the oxidation process to continue and spread.
Vulnerable Areas
Certain parts of a car are more susceptible to rust due to their exposure to environmental elements. These include:
– Door Sills: Often exposed to road salt and moisture.
– Wheel Arches and Fenders: Constantly bombarded by debris and moisture from the road.
– Front Edge of the Hood: Vulnerable to stone chips and road debris.
– Edge of the Trunk: Can trap water and moisture.
– Junction Points of Elements: Where panels meet, water can seep in and start the rusting process.
Preventive Measures
To prevent corrosion, regular maintenance and care are essential:
- Regular Washing: Clean your car at least three to four times a month. Washing removes dirt, salt, and other contaminants that can accelerate rust formation.
- Inspections: Regularly inspect the car, preferably on a lift or overpass, to detect early signs of rust. Look for bubbling paint, which can indicate rust forming underneath.
- Anti-Corrosion Treatment: Apply anti-corrosion treatments soon after purchasing the car. These treatments often involve applying a protective coating to vulnerable areas, such as the underbody and wheel arches.
- Storage: Store the car in a warm, stable environment to avoid moisture buildup. A climate-controlled garage is ideal.
- Prompt Repairs: Treat and paint over any chips or scratches immediately to prevent rust formation. Use touch-up paint and rust inhibitors to seal the damaged areas.
Treatment of Damaged Areas
If you notice chips or scratches, treat the damaged areas with special compounds and repaint them. This helps to seal the exposed metal and prevent rust from developing. The treatment process typically involves:
- Cleaning: Remove dirt, debris, and loose rust from the affected area.
- Rust Converter: Apply a rust converter to neutralize the rust and prevent it from spreading.
- Priming: Use a primer to create a smooth surface for the paint.
- Painting: Apply touch-up paint to match the car’s color.
- Sealing: Use a clear coat to protect the new paint layer.
Rust and Climate in the UAE
In the UAE, cars can be susceptible to rust for specific reasons:
- Lack of Anti-Corrosion Treatment: Many vehicles are not adapted to local conditions and lack protective coatings. This can leave the metal vulnerable to the harsh desert environment.
- Salt and Water Exposure: Saltwater and salty air can accelerate corrosion. Coastal areas, in particular, pose a risk due to the high salt content in the air.
- Open-Air Parking: Exposure to the elements can lead to fading, paint damage, and eventually rust. Sand can also cause abrasions on the paint surface, leading to rust.
Despite the arid climate, weak paintwork and sand can still contribute to rust development in UAE cars. The intense heat can cause the paint to crack, creating entry points for moisture.
Susceptible Car Models
Certain foreign car models are more prone to rust:
- Japanese Cars: Often have thin paint coatings that wear quickly, making them more susceptible to rust.
- Korean Cars: Slightly better paintwork but lower quality metal, which can still rust over time.
- Chinese Cars: Generally use low-quality metal that corrodes quickly, even with proper paint application.
- German Premium Cars (BMW, Audi, Mercedes-Benz): Known for higher quality paint layers and materials, offering better resistance to rust. However, even these cars are not immune to corrosion if neglected.
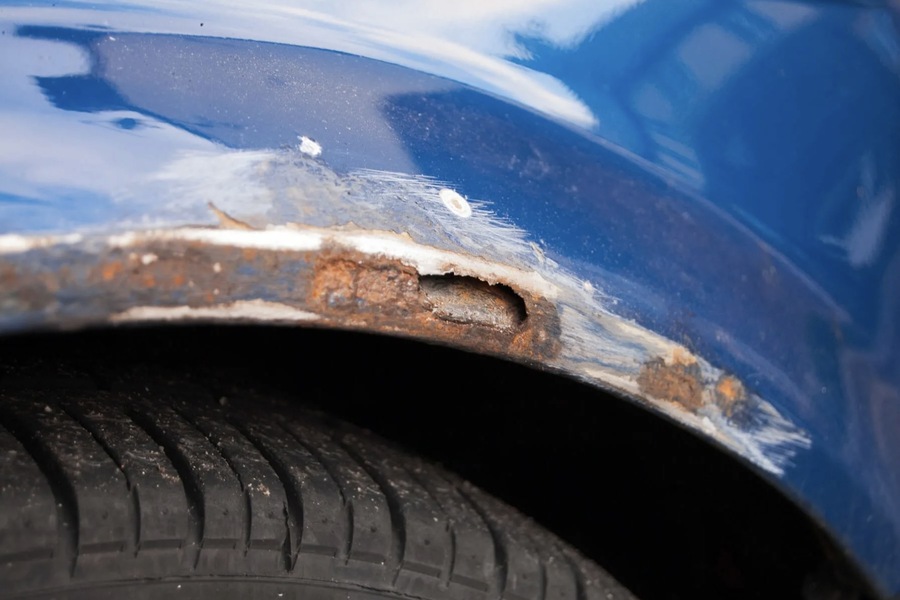

Protective Measures
To protect your car from rust:
- Anti-Corrosion Treatment: Apply specialized compounds to the underbody, wheel arches, and accessible cavities. These treatments form a barrier that prevents moisture and salt from reaching the metal.
- Anti-Gravel Film: Use this film to protect the paintwork from chips and water access. The film acts as a sacrificial layer, absorbing impacts that would otherwise damage the paint.
- Wax Application: Regularly apply wax to a clean, dry surface for added protection. Wax creates a hydrophobic layer that repels water and reduces the risk of rust.
- Corrosion Inhibitors: Use these substances to slow down or stop the corrosion process. Corrosion inhibitors can be sprayed onto vulnerable areas to create a protective barrier.
- Galvanization: Apply a thin layer of zinc to the steel for long-term protection. Galvanized steel is much more resistant to rust due to the sacrificial nature of zinc, which corrodes before the steel.
Annual Checks
Check the condition of your car’s coating annually, preferably in spring, and update the protection as needed. Spring is ideal because it follows the winter months when salt and moisture exposure is highest.
Safety Precautions
When working with anti-corrosion compounds, always use protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and a respirator. For best results, consider hiring a professional to handle the treatment. Professionals have the tools and expertise to apply protective coatings effectively.
By understanding the causes, types, and preventive measures for rust, you can effectively protect your car and extend its lifespan. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are key to preventing rust from compromising your vehicle’s integrity. With proper care, your car can remain rust-free and retain its value for many years.
I am an accomplished coder and programmer, and I enjoy using my skills to contribute to the exciting technological advances that happen every day at Oswald Tech.
